When it comes to dentistry, carving burs are an invaluable rotary cutting tool. From chiseling away dead tooth structure to shaping and smoothing existing structures, carving burs are a staple among dental practitioners. Their use is varied and their design comes in all shapes and sizes. Most commonly, they are crafted from steel with a cylindrical shape, but other materials may also be utilized depending on the needed result.
A handpiece, driven by a dental drill and its subsequent foot pedal control, is the enabling factor for plentiful carving capabilities. Essentially, these tools provide the power necessary to turn cutting implements like burs, enabling artisans to craft with finesse.
With meticulous precision, the dentist grips the handpiece and manipulates the bur with their other hand. By exerting just the right amount of pressure to the bur, they are able to achieve the desired level of cut.
Crafting burs can be employed to extract tooth elements or fashion tooth structures. Whenever taking away tooth structure, the bur should be kept perpendicular to the tooth’s exterior and be moved in an oscillating action. The amount of tooth structure that gets eliminated relies on the bur’s measurements and form.
In order to give shape to teeth, the bur is kept inclined to the tooth’s outer layer and guided in circular motions. How much of the tooth surface is reduced depends on the size and contour of the bur used.
Through the use of a bur – a cylindrical file-like device – dental restoration can be deftly extracted, the degree depending on the size and design of the bur itself. Working perpendicular to the tooth, one would move the bur back-forth, thus resulting in a smooth removal of the restoration.
There are a variety of carving burs to pick from, depending on your task. Your three main choices are cylindrical, conical, and ball-shaped – the size of each bur is determined by the thickness of the cutting edge.
When it comes to bur size, the material it’s made from plays a significant role. Steel is the durable material of choice for those looking for the largest burs available. Opting for burs constructed of carbide produces options that are sized slightly smaller than steel, while diamond burs provide the smallest form factor.
The cutting trajectory of a bur is excellent connected to the material it’s crafted from. Burs formed from steel are extremely tenacious, splendid for erasing large parts of tooth architecture. Carbide-made burs are comparatively mild, perfect for eliminating minor proportions of tooth constitution. As for diamond-crafted burs, they are the least coercive and excel in trimming the contours of tooth construction.
Depending on the shape of the bur, it determines how aggressive the bur is when used on tooth structure. The most powerful is the cylindrical bur, capable of taking down sizable amounts of tooth structure with ease. Then there’s the conical bur, which is a bit less extreme and suited to smaller amounts of structure removal. Finally, we have ball-shaped burs which are the least abrasive option and best for detailed sculpting of tooth structure.
The specific size and design of a carving bur play a central role in its selection process. Additionally, the material it is crafted from contributes considerably to its functionality. Therefore, the shape of the bur should be carefully assessed to ensure it has the capacity to cut precisely as intended.
Related Product
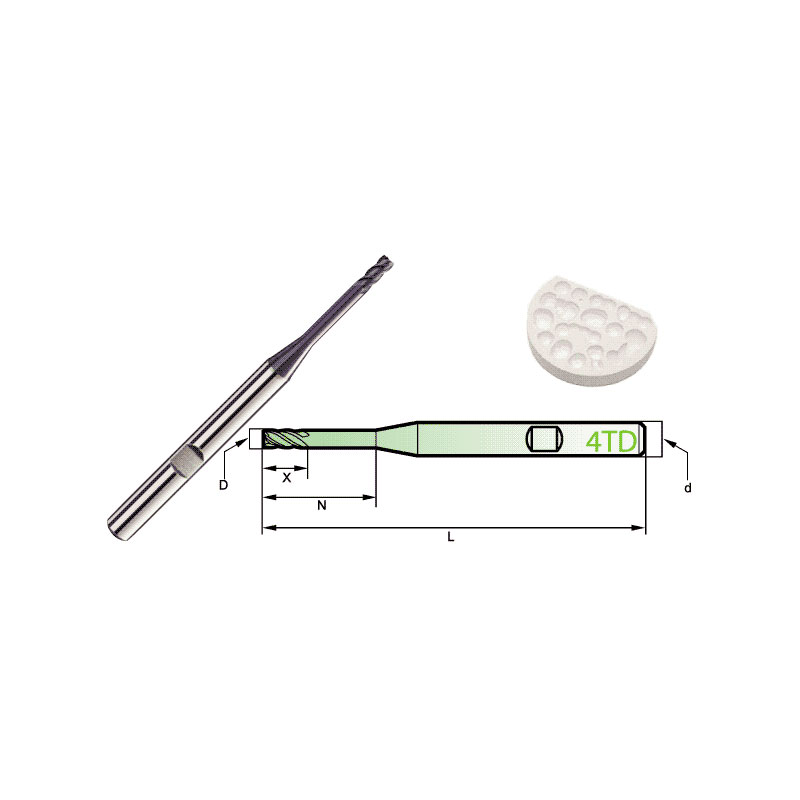
Carbide Roland CAD/CAM Burs
Product Information Origin Tianjing, China Brand MSK Number Of Blades 4 Product Name Dental Special 4-Blade End Mill Model D Number Of Blades Z X N L d 4TD2060HB 2 4 […]
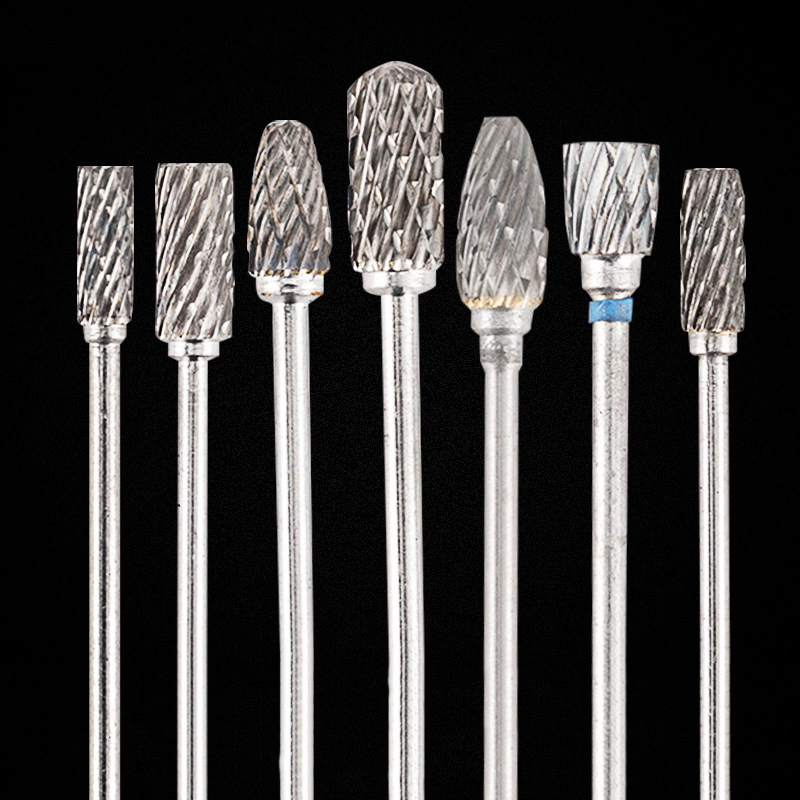

HP Deburring Carbide Burs
Product Information Brand MSK Material Tungsten Steel Model Grinding Head Custom Processing Yes Feature: The dental grinding head is made of tungsten steel with stabl […]
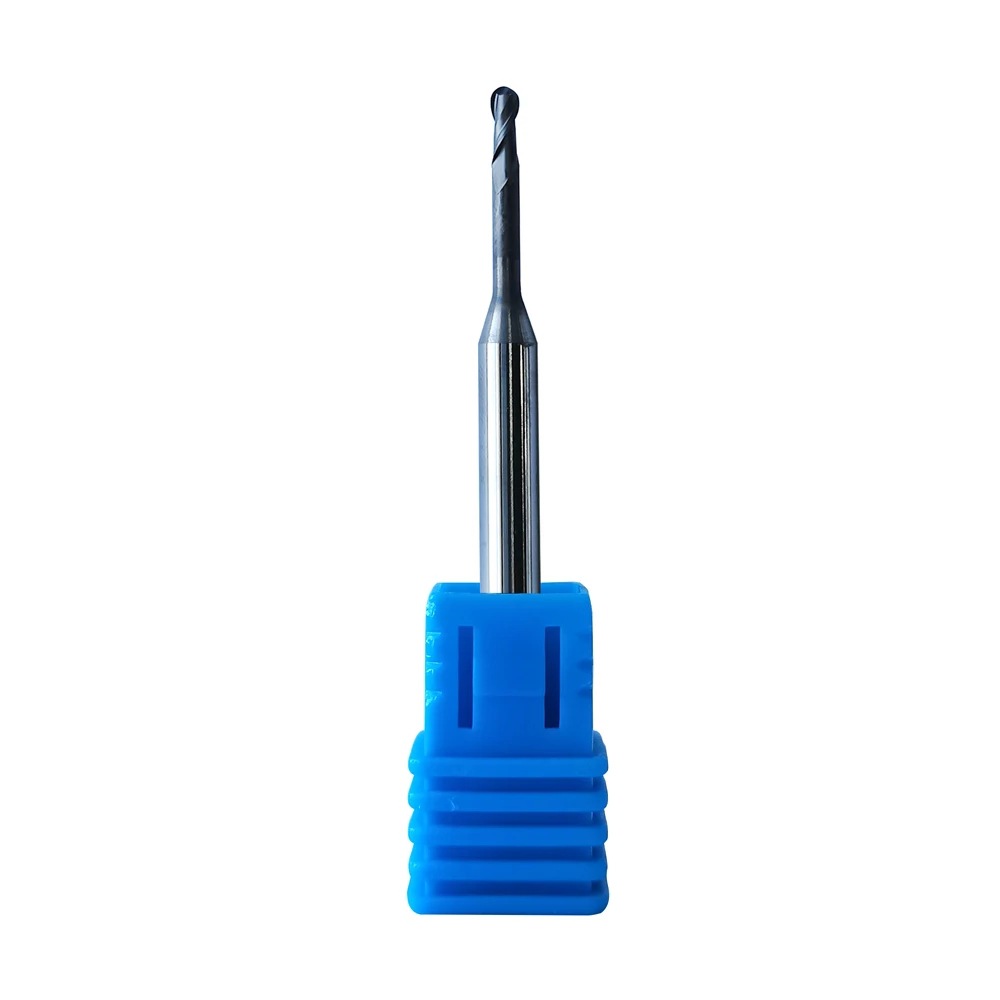

Supply Roland DLC Zirconia Burs
Product Information Origin Tianjing, China Series Dental Bur Brand MSK Cutting Edge Form 2 Blade/3 Blade Ball Diameter (Mm) 0.6, 1, 2 Material Very Fine Grained Cemented Car […]

Step Bur Milling Bur Grinder for Glass Cerami
Product Information Origin Tianjing, China Shank Diameter 1.8 (mm) Brand MSK Scope Of Application CEREC3 Grinding Equipment Material Stainless Steel/Carbide Main Sales Areas […]

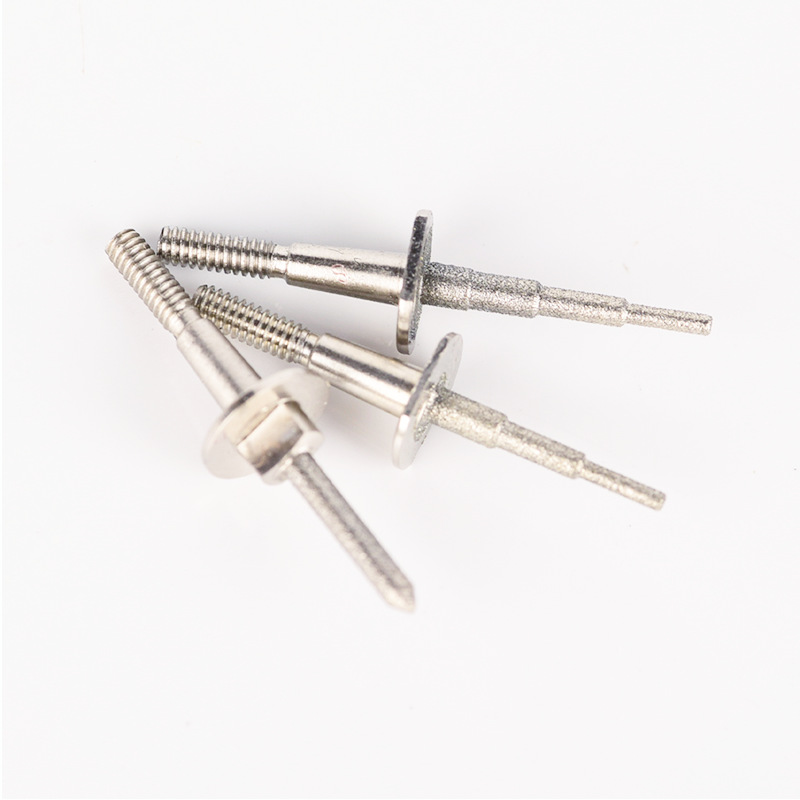
Diamond Coating Round Diamond Cutters
Product Information Origin Tianjing, China Series U Series Brand MSK Cutting Edge Form Helical Structure Ball Diameter (Mm) 3 Material Carbide Minimum Cutting Diameter At Th […]

Dental CAD/CAM Milling Burs
Product Information Origin Tianjing, China Material Stainless Steel Brand MSK Applicable Machine Tools A Variety Of Options Custom Processing Yes Whether To Coat No Is It a […]
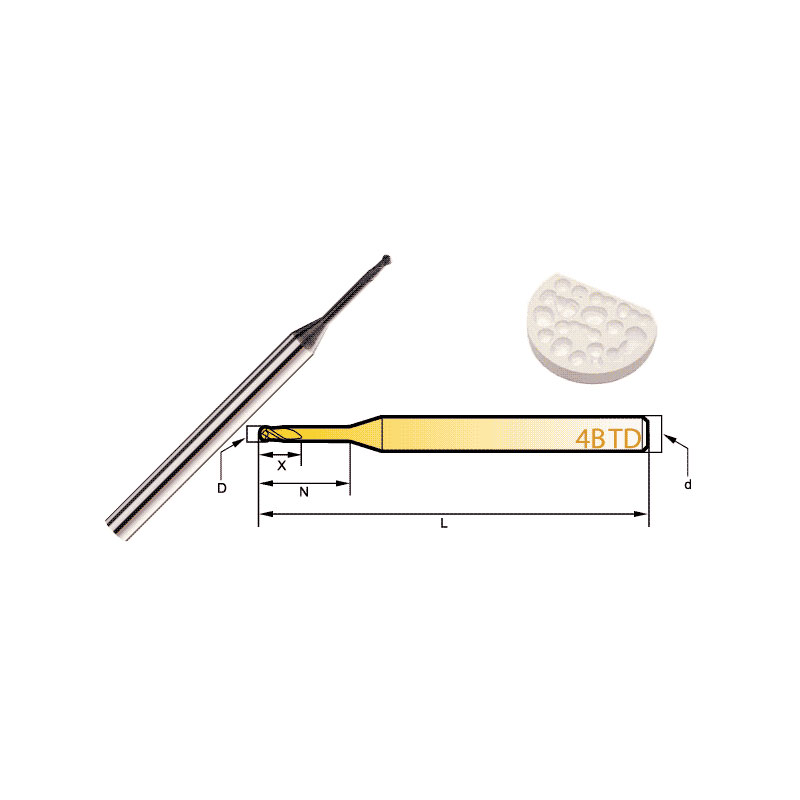
Diamond Bur Ball Round
Product Information Product Name Dental 4-Flute Ball End Mill Brand MSK Model D Number Of BladesZ X N L d 4BTD2060 2 4 6 6 50 3 4BTD2010 2 4 6 10 50 3 4BTD2016 2 4 6 […]
Post time: 2023-06-29
