It is essential to select carbide burs for machining purposes that match the material’s characteristics. There is a range of carbide varieties with various features, so the ideal bur used for one material may not be the perfect choice for another. Those that are specifically crafted for each material provide the highest quality results.
Carbide burs designed to produce optimal cutting results are characterized by a sharp edge and a robust body. Additionally, these burs are built to reduce the tremors and noise generated during application.
Of all varieties of carbide, tungsten carbide is the biggest culprit in CAD CAM burs. Its extreme hardness and superior melting point have earned it great renown, as have its many wear- and shock-resistant properties.
Possessing impressive temperature and hardness properties, titanium carbide stands out as a suitable material for CAD CAM burs. While it cannot boast the wear-resistance of tungsten carbide and may not be as shock resilient, it still offers remarkable advantages in terms of its melting point and durability.
Complementing tungsten carbide, cobalt is sometimes used in CAD CAM burs, boasting a higher melting point. Although it is more durable than its aforesaid counterpart, it lacks the same ability to resist wear and shock.
With its robust properties, carbide plays an essential role in modern manufacturing. However, not all carbide burs are produced equally – different types of carbide are optimized for mechanical applications on different materials. When selecting a CAD CAM carbide burr, make sure to research the product thoroughly for the material being machined for the best results.
Sharp cutting edges and robust body structures make the most effective carbide burs, as they are specially made to reduce shakiness and vibration.
For machining and fabricating applications, tungsten carbide is the go-to type of carbide. Its hard-as-nails composition allows it to stand up to wear and tear, and its melting point is remarkably high—making it perfect for CAD CAM burs. It also has excellent shock resistance, so you can rely on it under pressure.
Impressive for its heat and melting capacity, titanium carbide may be employed in CAD CAM burs, though it can’t match tungsten carbide in terms of its resistance to wear and shock.
The use of cobalt in CAD CAM burs is not uncommon. A harder material than tungsten carbide and boasting a much higher melting point, it is more susceptible to wear and shock than its tungsten counterpart.
Related Product
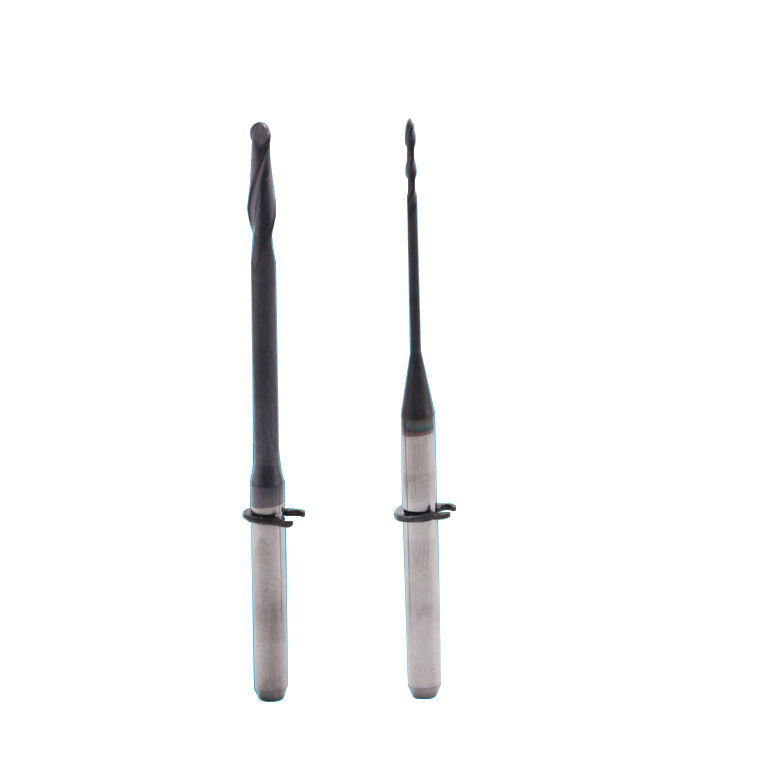

Dental CAD/CAM Milling Burs
Product Information Origin Tianjing, China Material Stainless Steel Brand MSK Applicable Machine Tools A Variety Of Options Custom Processing Yes Whether To Coat No Is It a […]

Step Bur Milling Bur Grinder for Glass Cerami
Product Information Origin Tianjing, China Shank Diameter 1.8 (mm) Brand MSK Scope Of Application CEREC3 Grinding Equipment Material Stainless Steel/Carbide Main Sales Areas […]

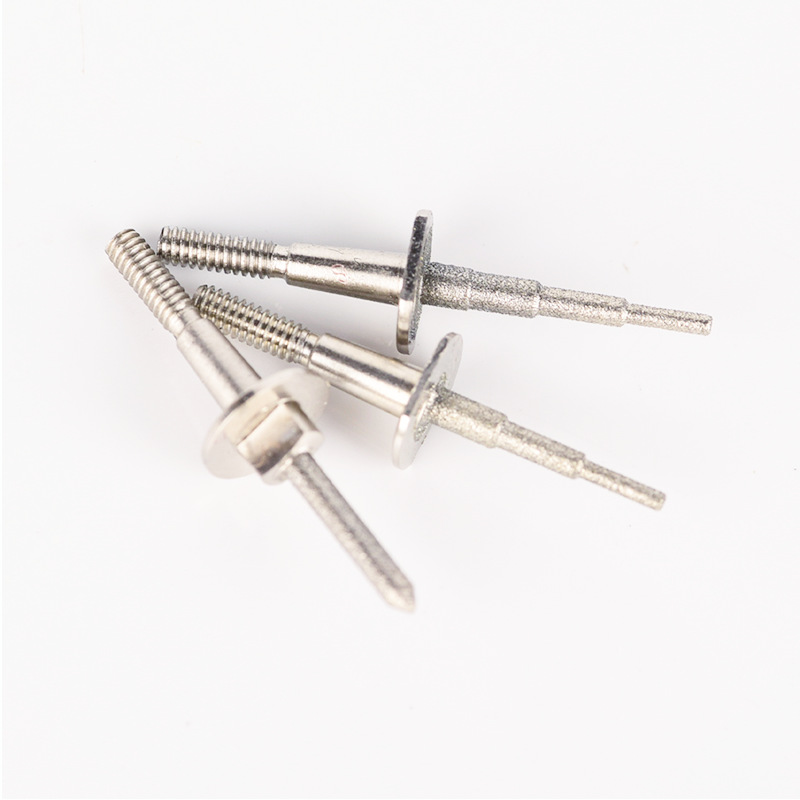
Diamond Coating Round Diamond Cutters
Product Information Origin Tianjing, China Series U Series Brand MSK Cutting Edge Form Helical Structure Ball Diameter (Mm) 3 Material Carbide Minimum Cutting Diameter At Th […]
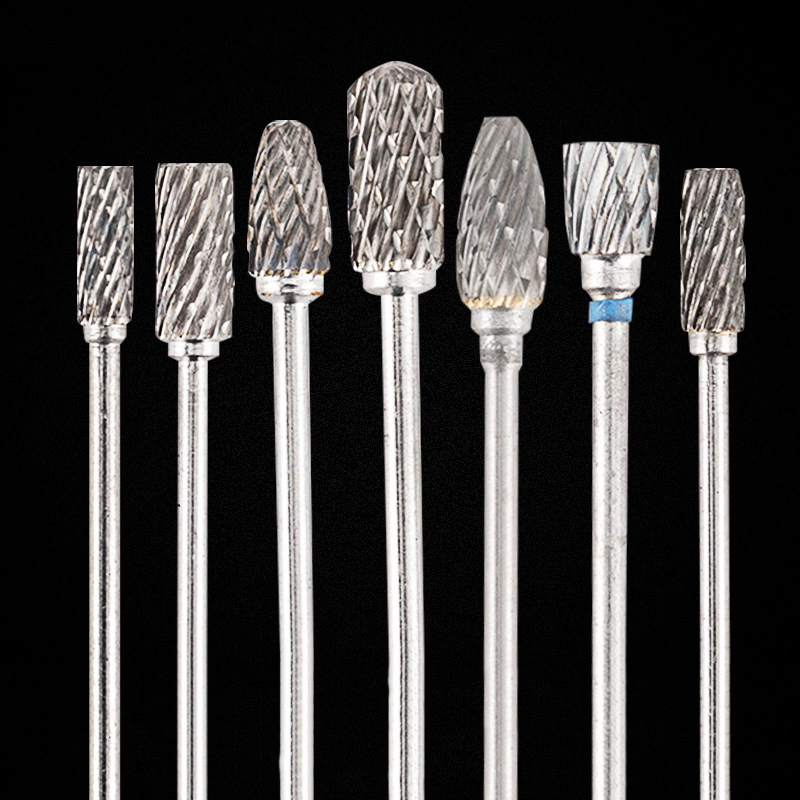

HP Deburring Carbide Burs
Product Information Brand MSK Material Tungsten Steel Model Grinding Head Custom Processing Yes Feature: The dental grinding head is made of tungsten steel with stabl […]
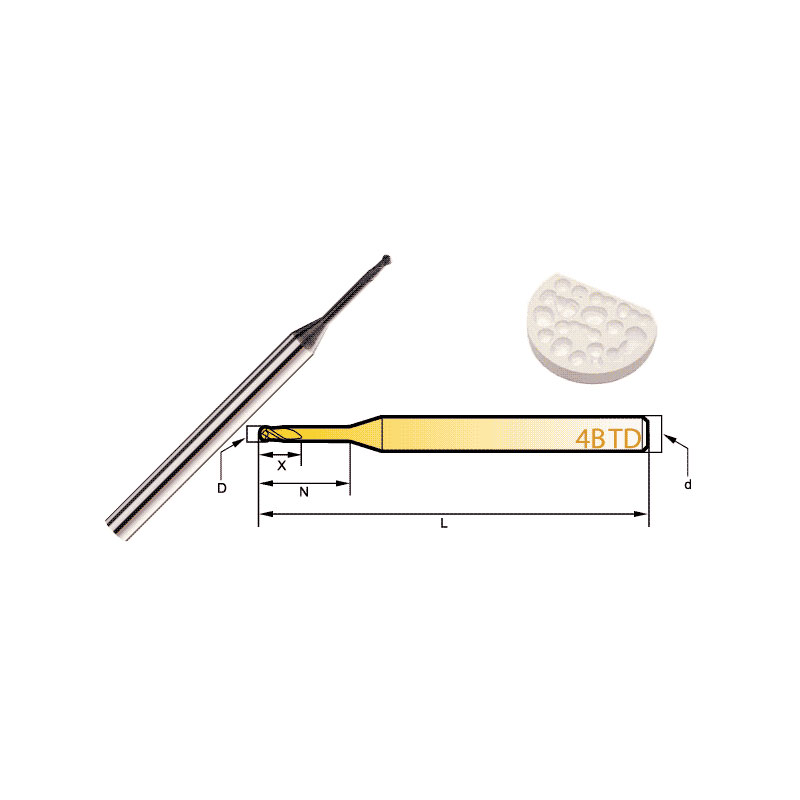
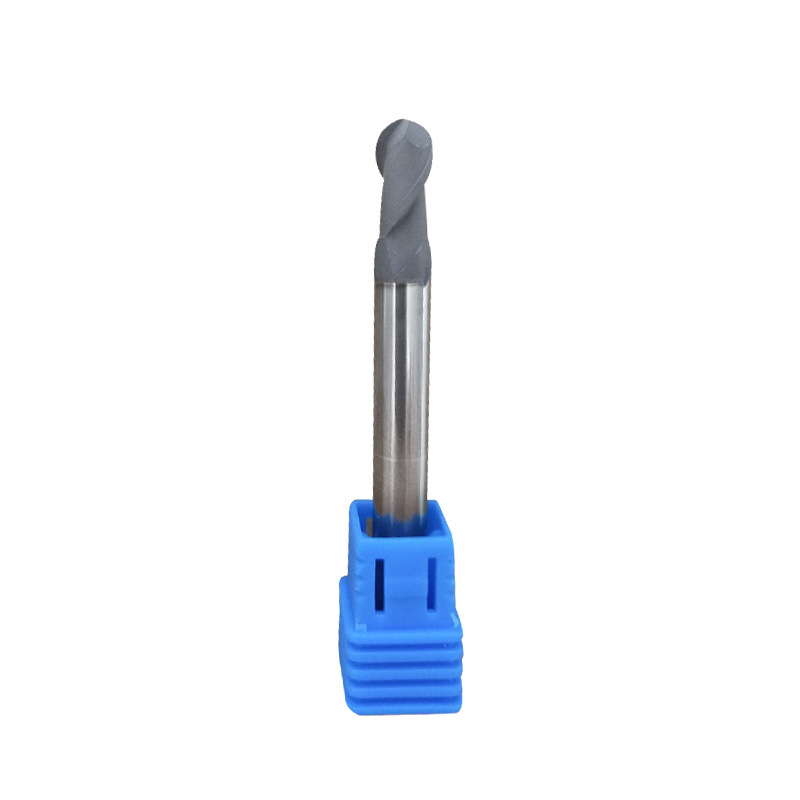
Diamond Bur Ball Round
Product Information Product Name Dental 4-Flute Ball End Mill Brand MSK Model D Number Of BladesZ X N L d 4BTD2060 2 4 6 6 50 3 4BTD2010 2 4 6 10 50 3 4BTD2016 2 4 6 […]
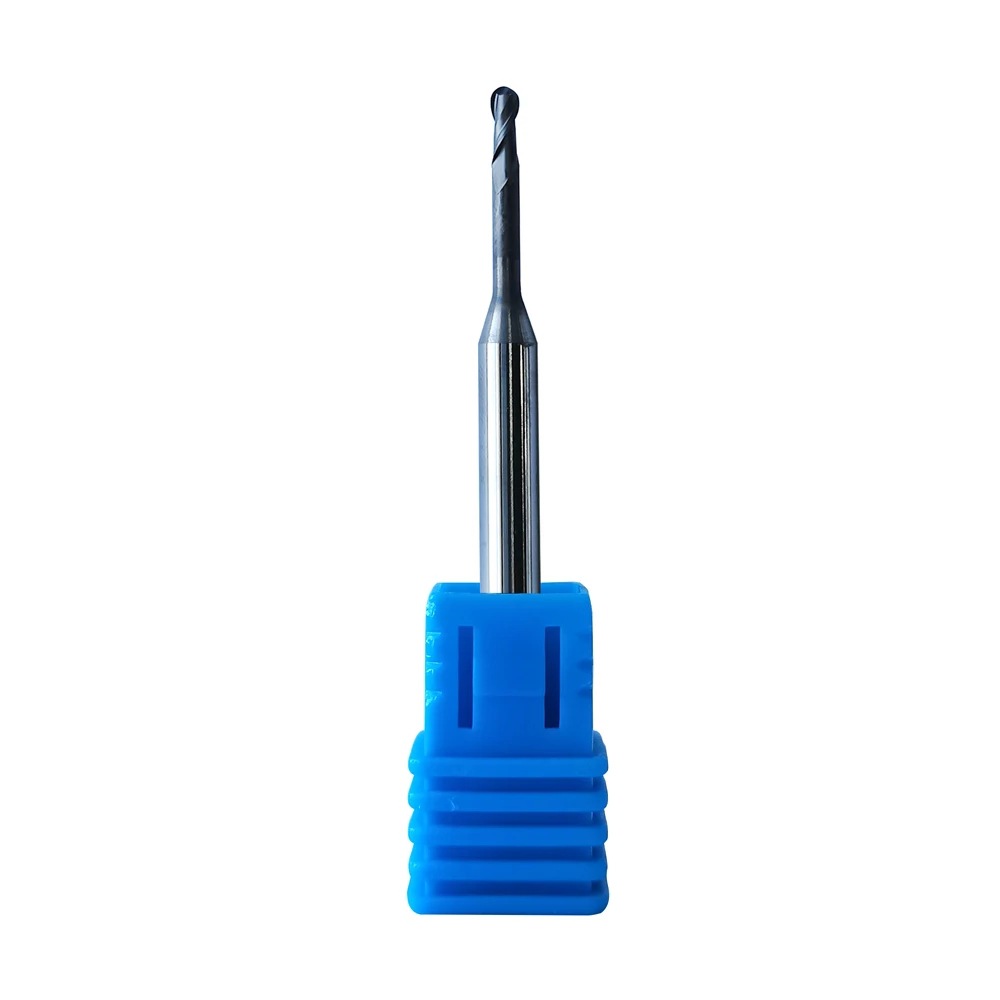

Supply Roland DLC Zirconia Burs
Product Information Origin Tianjing, China Series Dental Bur Brand MSK Cutting Edge Form 2 Blade/3 Blade Ball Diameter (Mm) 0.6, 1, 2 Material Very Fine Grained Cemented Car […]
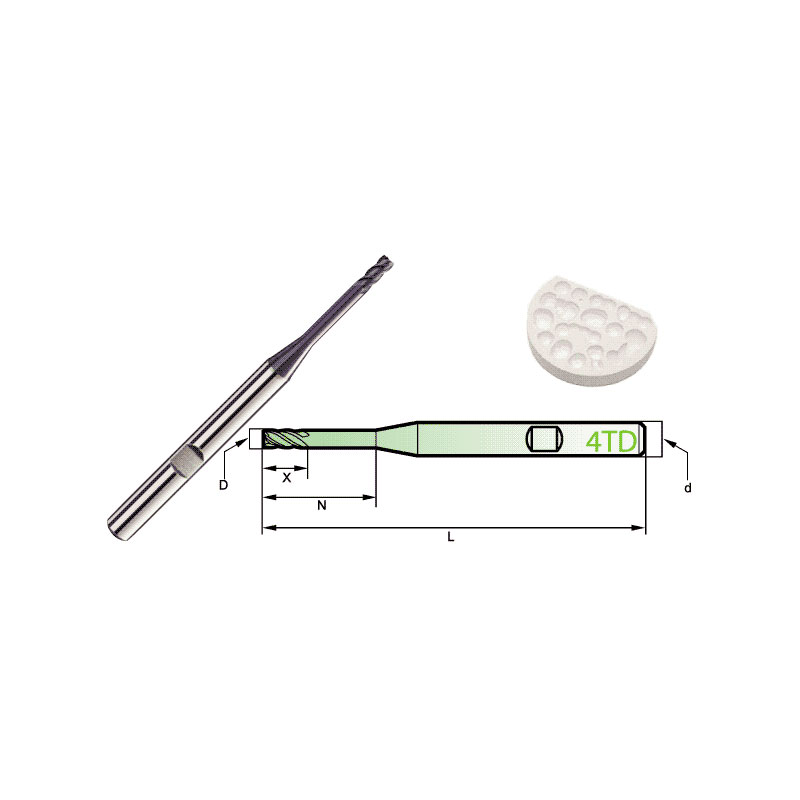
Carbide Roland CAD/CAM Burs
Product Information Origin Tianjing, China Brand MSK Number Of Blades 4 Product Name Dental Special 4-Blade End Mill Model D Number Of Blades Z X N L d 4TD2060HB 2 4 […]
Post time: 2023-06-25
